In data storage, a tape library is a system comprising magnetic tape cartridges and drives, used for long-term data preservation and backup.
Tape libraries vary widely in cost and sophistication. Typically, a library includes multiple tape drives for data read/write operations, access ports for adding and removing tapes, barcode tracking, and robotic mechanisms for mounting and dismounting cartridges. Libraries can accommodate thousands of tapes, scaling to meet diverse data needs.
While tape technology has evolved significantly in reliability and functionality, the core principle of storing data on magnetic tape remains stable. A tape library’s compatibility with an organisation’s backup software is essential, and vendors typically provide compatibility guides to ensure seamless integration.
When selecting a tape library, organisations must account for factors like the size of the backup or archival set, expected data growth, and specific requirements within their data protection system.
Though the advent of high-capacity disks and cloud storage has impacted tape’s popularity, it remains a cost-effective and reliable choice for archiving. Technologies like the Linear Tape File System (LTFS) add a file system layer to the library, enhancing its suitability for archival.
A tape library offer lower costs than disk or flash systems, particularly for archival needs, where tape’s long shelf life and durability make it ideal. Tapes are also resilient in disaster recovery scenarios, providing an additional layer of security. Most modern libraries include encryption options, protecting data both in-house and when transported off-site.
With individual tape cartridges offering capacities of up to 45 TB (compressed), tape libraries are well-suited to handle large-scale, infrequently accessed data. While tape retrieval is typically slower than disk, advances in robotics continue to improve access speeds.
Organisations of all sizes use tape libraries, with large enterprises often deploying them for secondary backup or as a dedicated archival solution. Automated libraries streamline data retrieval, making them an effective tool for managing vast amounts of information.
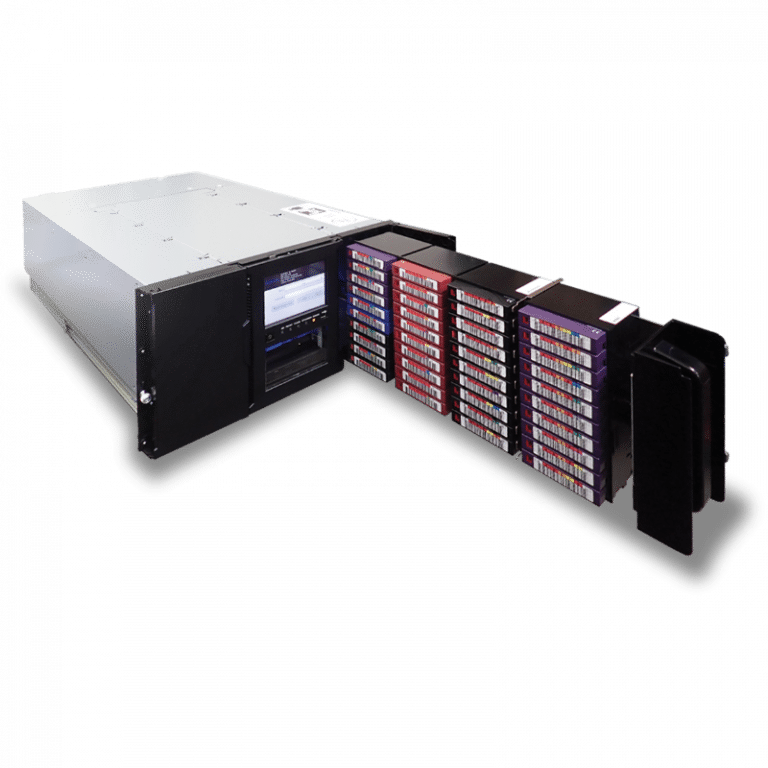
Tape libraries and autoloaders automate archival processes across multiple tapes. Autoloaders are less costly but lack the advanced capabilities of full libraries. A VTL, by contrast, uses disk-based storage that emulates a tape library, achieving faster write/read speeds while retaining the sequential data access structure.
Since StorageTek’s original tape library innovations, numerous enhancements have emerged. IBM pioneered LTFS for easier data access, while Oracle, Overland, Quantum, and Spectra Logic continue to release scalable, high-capacity libraries. Recent developments include Quantum’s Ransom Block for cyber protection and IBM’s Diamondback libraries, which supports up to 27 PB of storage.
The extensive capacity and reliability of tape libraries make them invaluable for large-scale archival projects. For instance, Nascar Productions used a Spectra Logic libraries to archive 180,000 hours of video footage, while NBC Olympics used Spectra tape libraries for their disaster recovery and video archiving needs during the 2016 Rio Olympics.
Smarter, strategic thinking.

Keep me up-to-date with news and announcements regarding LTO Ultrium Tape.
I consent to the Privacy Policy.